Over-the-Counter Laxatives: What They Are and How They Help
When dealing with occasional constipation, many turn to over-the-counter laxatives, medications you can buy without a prescription that help move stool through the intestines. Also called OTC laxatives, they range from gentle stool softeners to fast‑acting stimulants. Stool softeners, agents that add moisture to soften the stool work by reducing friction, while fiber supplements, bulk‑forming products that increase stool volume add natural bulk. Stimulant laxatives, compounds that trigger intestinal muscle contractions and osmotic laxatives, substances that draw water into the colon provide quicker relief. Understanding these options lets you pick the right tool for your needs.
How Different Types Fit Into a Constipation Plan
Every laxative type fills a specific role. Fiber supplements encompass natural sources like psyllium, which swell and create a gentle push, ideal for daily maintenance. Stimulant laxatives such as senna or bisacodyl are the go‑to when you need rapid action, but they can cause cramping if overused. Osmotic agents like polyethylene glycol pull water into the bowels, softening stool without stimulating muscles directly—great for people who dislike the jittery feeling of stimulants. Stool softeners, for example docusate sodium, focus on lubricating the stool, making it easier to pass without increasing bulk. Choosing the right category depends on how quickly you need relief and whether you prefer a mild, ongoing solution or a strong, short‑term boost.
One key rule is to match the laxative’s mechanism to your body’s signals. If you notice hard, pebble‑like stools, a fiber supplement or stool softener often does the trick. When stools are stuck and you feel a pressing need, a stimulant or osmotic laxative may be more effective. Also, remember that dehydration can worsen constipation, so pairing any OTC laxative with plenty of fluids boosts results. This simple combo—right product plus water—covers most everyday scenarios without a doctor’s visit.
Safety matters, too. Most experts agree that using stimulant laxatives for more than a week can lead to dependence, where the colon relies on the drug to move. Osmotic laxatives are generally safe for short periods but can cause electrolyte shifts if taken in high doses. Fiber supplements are the least likely to cause side effects, though they can cause bloating if you jump in too fast. Start low, increase gradually, and watch how your body reacts. If you have a chronic condition like IBS, kidney disease, or heart failure, check with a pharmacist before picking a product.
Beyond the basics, there are niche options worth mentioning. Magnesium‑based laxatives combine osmotic action with a mineral that many people need, while herbal blends like cascara or aloe offer a more natural stimulant effect. Some OTC combos pair a stool softener with a stimulant to give a balanced push—think of them as a two‑step plan in one pill. Knowing these nuances can save you time and money, helping you avoid trial‑and‑error purchases.
When you shop, look for clear labeling that shows the active ingredient, dosage, and intended use (e.g., “quick relief” vs. “daily fiber”). Avoid products that hide their contents behind vague terms; transparency helps you compare potency and side‑effect profiles. Also, store any laxatives away from heat and moisture to keep them effective. A tidy medicine cabinet makes it easier to grab the right item when you need it most.
Below you’ll find a curated list of articles that dig deeper into each laxative class, compare popular brands, and offer step‑by‑step guides for safe use. Whether you’re curious about fiber supplements, need a fast‑acting stimulant, or want to understand osmotic laxatives, the posts ahead give practical tips you can apply today.
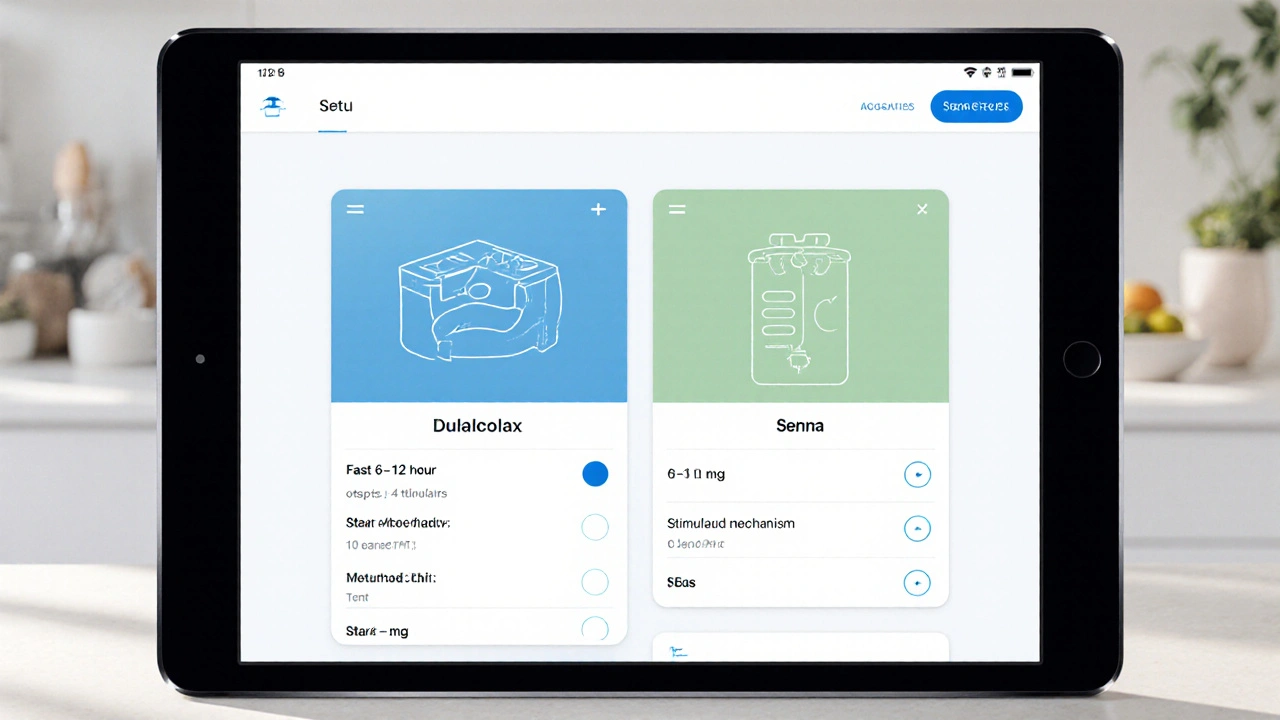
Dulcolax (Bisacodyl) vs Common Alternatives - Complete Comparison
A detailed side‑by‑side comparison of Dulcolax (bisacodyl) with common constipation remedies, covering onset, mechanism, dosage, side‑effects, cost and how to choose the right option.