Narrow Therapeutic Index: What It Means and Why It Matters for Your Medications
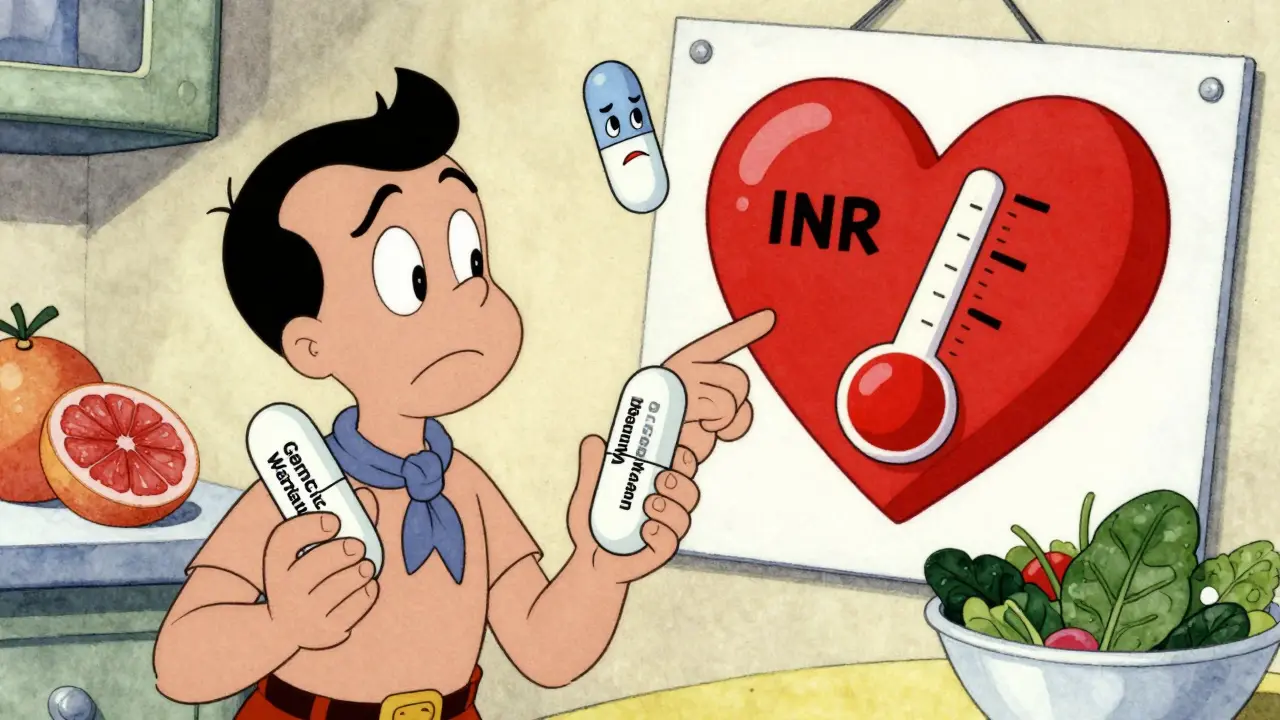
When a drug has a narrow therapeutic index, the difference between a safe dose and a harmful one is very small. Also known as a narrow therapeutic window, this means your body can’t handle much variation — too little and the drug doesn’t work, too much and it could hurt you. This isn’t just a technical detail. It’s a life-or-death factor for people taking medications like warfarin, lithium, digoxin, or phenytoin. These aren’t rare drugs. Millions use them daily, and many don’t realize how precise their dosing needs to be.
Drugs with a narrow therapeutic index don’t play nice with other meds, foods, or even changes in your health. If you start a new antibiotic, your kidneys slow down, or you eat more leafy greens, your drug levels can swing dangerously. That’s why regular blood tests are often required — not just to check if it’s working, but to make sure it’s not poisoning you. The therapeutic window, the range between the minimum effective dose and the minimum toxic dose for these drugs is razor-thin. One milligram too much can cause seizures, irregular heartbeat, or kidney damage. One milligram too little might let your seizure, blood clot, or heart failure come roaring back.
This is why generic versions of these drugs aren’t always interchangeable. Even small differences in fillers or how fast the pill breaks down can push you out of the safe zone. That’s not a flaw in generics — it’s a feature of the drug itself. The FDA, the agency that oversees drug safety in the U.S. requires extra testing for these drugs, but you still need to be your own advocate. Never switch brands without talking to your doctor. Never skip blood tests. And never assume a new prescription is safe just because it’s the same name as your old one.
People with kidney or liver problems are at higher risk. So are older adults. And anyone taking multiple medications — especially if one of them affects how your body processes the drug. That’s why comorbidities and polypharmacy are such big concerns with narrow therapeutic index drugs. A simple change, like starting a new blood pressure pill, can throw off your lithium levels. A cold medicine with an antihistamine can interfere with your seizure control. That’s why the drug interactions, how one medicine changes how another behaves in your body section in your prescription guide isn’t just fine print — it’s your safety net.
You’ll find posts here that break down exactly how these drugs behave, what to watch for, and how to avoid mistakes. From how to read your lab results to why your pharmacist might refuse to substitute a generic, this collection gives you the real-world tools to stay safe. No jargon. No fluff. Just what you need to know to make sure your medication does what it’s supposed to — without hurting you.
Drug Interaction Issues: When Generics Interact Unexpectedly
Generic drugs are just as safe as brand-name ones, but unexpected side effects can happen due to inactive ingredients or switching manufacturers. Learn how to spot real interaction risks and avoid common myths.
FDA Bioequivalence Standards for NTI Drugs: What You Need to Know
The FDA applies stricter bioequivalence standards for narrow therapeutic index (NTI) drugs like warfarin, phenytoin, and digoxin to prevent dangerous dosing errors. Learn how these rules differ from regular generics and what they mean for patients.