Benzodiazepines – What They Are and When They're Used
If you've ever been told to take a pill for anxiety or trouble sleeping, chances are it could have been a benzodiazepine. These drugs work fast by calming the brain’s activity, which makes them popular for short‑term relief of panic attacks, insomnia, muscle spasms, and sometimes seizure disorders. Because they act quickly, many people feel better after just one dose.
Common Benefits and Typical Prescriptions
Doctors usually write benzodiazepines for three main reasons: to ease acute anxiety, to help you fall asleep, or to relax tight muscles after an injury. Medications like diazepam (Valium), alprazolam (Xanax) and lorazepam (Ativan) are the most familiar names. They’re often given for a few weeks at most – enough time to get past a stressful event without staying on the drug forever.
When used correctly, these pills can be a lifesaver. A panic attack that feels like a heart attack can subside within minutes thanks to the calming effect. For people with severe muscle spasms, a single dose can let them move without pain. The key is following your doctor’s dosage instructions and not stretching the treatment beyond what’s advised.
Risks, Dependence & Safer Options
The downside of benzodiazepines is that they can build tolerance quickly. After a few weeks your body gets used to them, so you might need higher doses to feel the same effect. That habit often leads to dependence – you start craving the drug and experience withdrawal symptoms if you stop suddenly.
Common side effects include drowsiness, slowed reaction time, memory gaps, and occasional mood swings. Mixing these pills with alcohol or other sedatives can be dangerous because it amplifies the sleepy feeling and can suppress breathing.
If you’re worried about dependence, talk to your doctor about non‑benzodiazepine options. For anxiety, SSRIs like sertraline or therapy techniques such as CBT (cognitive behavioral therapy) work well over the long run. For sleep problems, melatonin supplements, good sleep hygiene, or short‑acting antihistamines can be safer choices.
When it’s time to taper off a benzodiazepine, do it slowly under medical supervision. A gradual reduction—cutting the dose by 10–25 % every week—helps minimize withdrawal symptoms like irritability, shaking, or insomnia.
Bottom line: benzodiazepines are powerful tools for short‑term relief but they aren’t meant to be a lifelong solution. Use them as your doctor suggests, watch for signs of tolerance, and explore safer alternatives if you need ongoing help with anxiety or sleep. Staying informed and keeping an open conversation with your healthcare provider is the best way to protect your health while getting the relief you need.
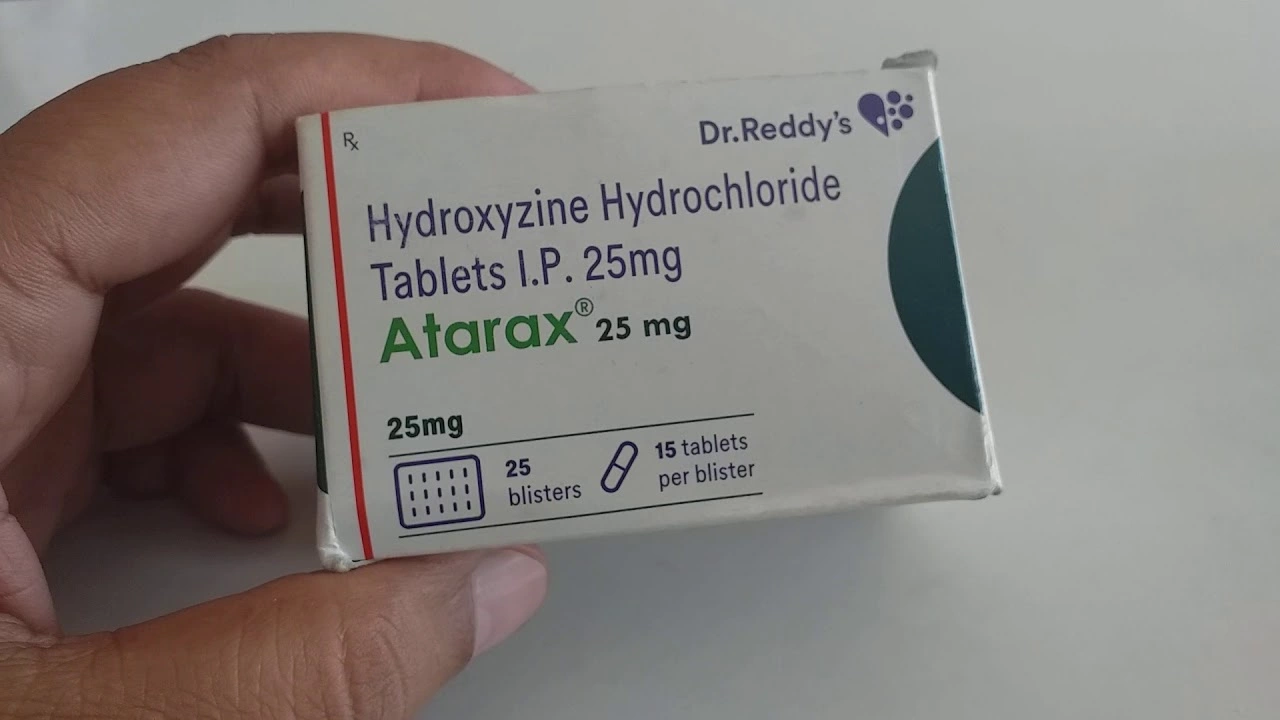
Hydroxyzine for Anxiety: A Natural Alternative to Benzodiazepines?
In my latest blog post, I explore the potential of Hydroxyzine as a natural alternative to Benzodiazepines for treating anxiety. I discuss its effectiveness, side effects, and how it works in comparison to traditional anti-anxiety medications. Additionally, I talk about the benefits of using a more natural option for those who prefer to avoid potentially addictive substances. I also share personal experiences and testimonials from people who have successfully used Hydroxyzine to manage their anxiety. Don't miss this informative and insightful discussion on a potential alternative treatment for anxiety.